Hey everyone! You know that feeling when you’ve been working on a project that you’re really excited about? Well, I can’t wait to share mine with you!
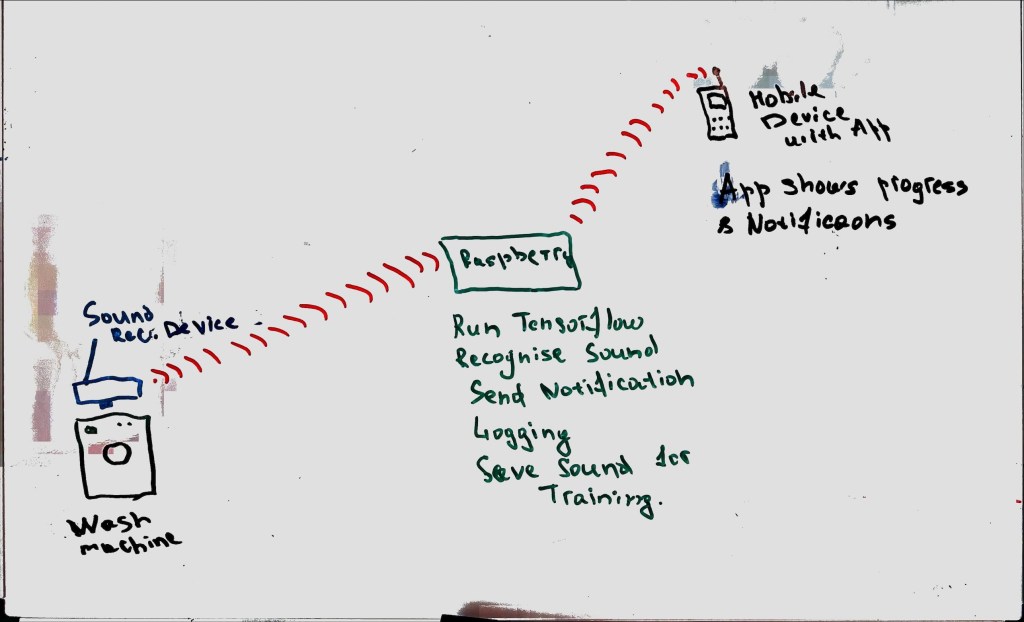
I’ve been building a TCP Server that receives .WAV files from a client and saves them to a special spot. To make things even more interesting, I’m using a clean architecture – keeping everything nice and neat in their own separate layers.
The Grand Design
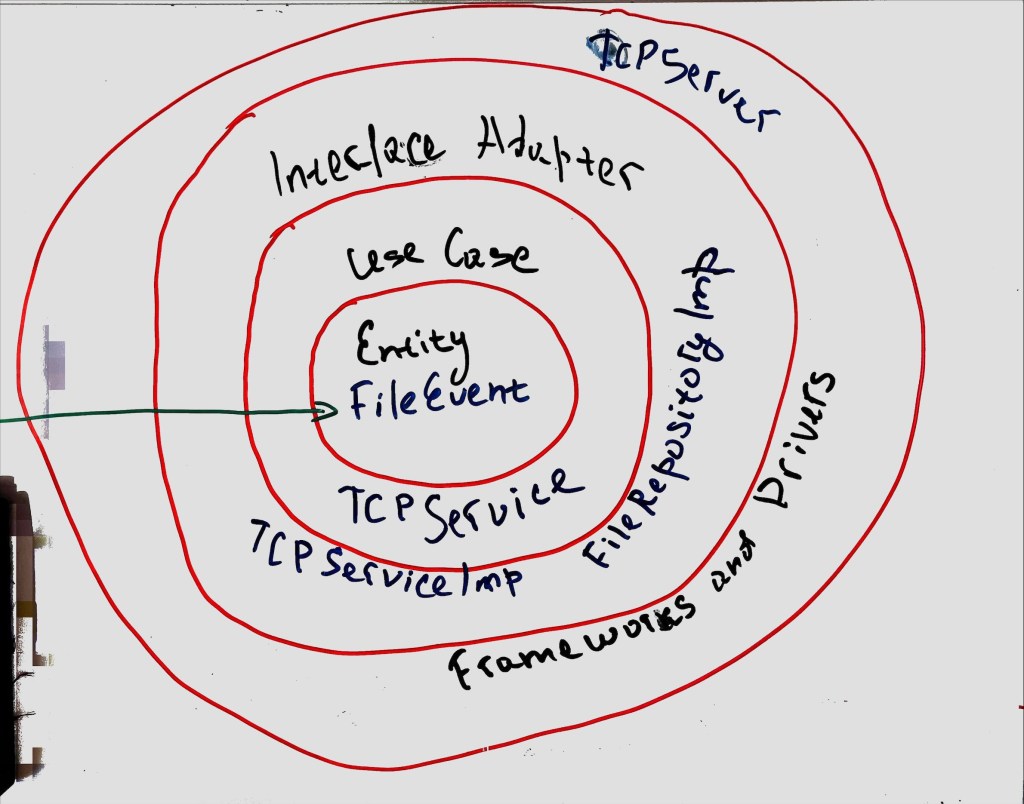
Let me take you on a tour of the architecture. Imagine a four-layer cake:
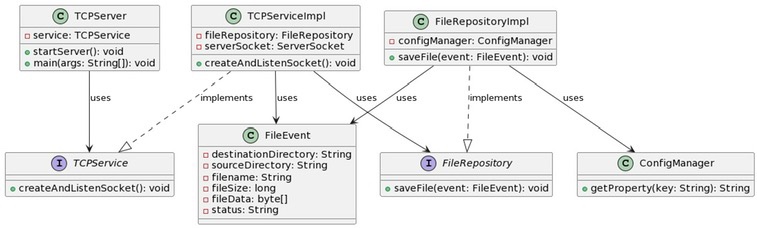
- Entities Layer: The heart of the cake (or application, in this case) is the FileEvent class.
- Use Cases Layer: The TCPService interface and its implementation, TCPServiceImpl, bring the action. They define and perform operations on our entities.
- Interface Adapters Layer: FileRepository and FileRepositoryImpl handle saving those .WAV files we’re receiving.
- Frameworks and Drivers Layer: Finally, at the top, we have TCPServer and ConfigManager. TCPServerlets us interact with the lower layers and ConfigManager keeps our settings in check.
Packaging Things Up
Inside this project, everything’s got its own home. I’ve got separate packages for different functionalities:
- com.smartmachine.tcpserver houses TCPServer TCPServer, the heart of the application.
- com.smartmachine.tcpserver.service is home to the service interfaces and their implementations.
- com.smartmachine.tcpserver.repositorycontains repository interfaces and their implementations.
- com.smartmachine.tcpserver.config keeps the configuration management classes.
- com.smartmachine.tcpserver.model is where the entity classes chill.
Meet the MVPs
Shoutout to the key components of my project:
- TCPServer: The entry point, it takes the help of TCPService to manage incoming client connections and file transfers.
- TCPService and TCPServiceImpl: The guts of the business logic – processing .WAV files sent over TCP.
- FileRepository and FileRepositoryImpl: The storage unit, they take care of storing the received .WAV files.
- ConfigManager: The settings master, handling everything from server port to output directory.
- FileEvent: Representing the data structure of the file event, including file data and metadata.
Keeping Things Running Smoothly
In any good adventure, you’ve got to plan for the unexpected. That’s why I’ve got basic error handling, ready for any hiccups like file not found, IO errors, and network errors.
Setting the Stage
And finally, all settings for the project are kept in a properties file. The trusty ConfigManager takes care of loading and accessing these settings.
UML Diagram